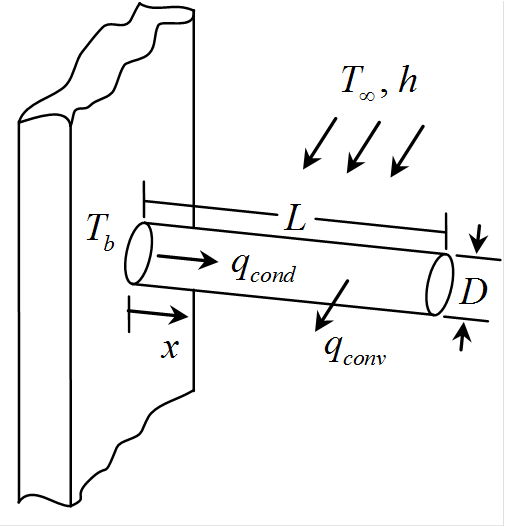
 Numerical
solution to the pin fin problem
Numerical
solution to the pin fin problem
Heat Equation: 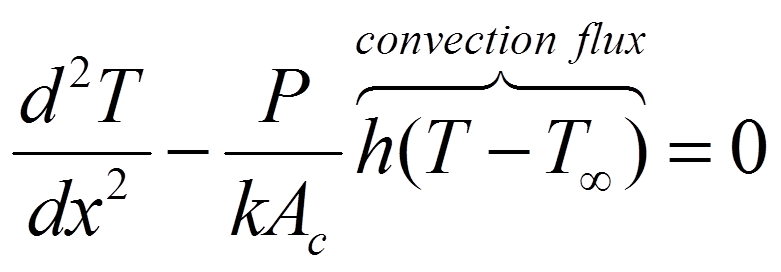
and boundary conditions:
BC1: ![]() and BC2:
and BC2: ![]() (convective tip) .
(convective tip) .
The heat equation can be integrated for the variables T and T'=dT/dx, as packaged into the vector:
![]()
Therefore, the heat equation may be expressed in terms of two first order equations:
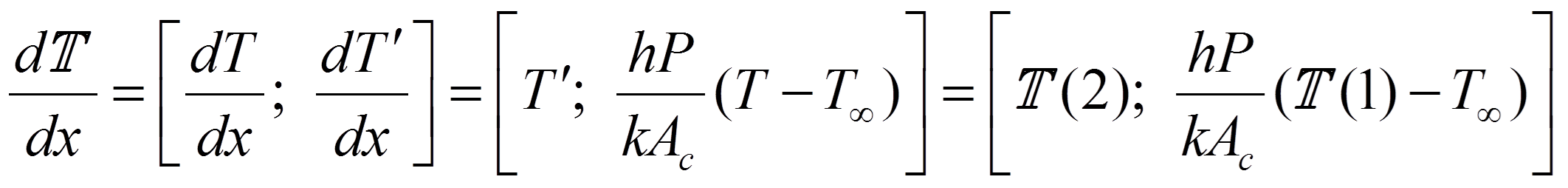
To numerically integrate these equations using a Runge-Kutta type solver requires both initial conditions:
![]()
However, since the initial temperature slope T'(0) is unknown, its value is guessed until the second known boundary condition, the "tip condition", is satisfied. This problem can be solved with the shooting method using the following steps:
L=0.15; D=0.01; k=50; h=40; Tb=500; Tinf=300; % problem parameters
Ac=pi*D^2/4; P=pi*D;
dTdx = @(T,x)[T(2); (P/k/Ac)*h*(T(1)-Tinf)]; % heat equation
TipBC=@(T)[k*T(2,end)+h*(T(1,end)-Tinf)]; % tip condition
dT0=-1000; % guess at initial slope
Integral = @(dT0)RK4(dTdx,[Tb; dT0],[0, L]); % handle for integration task
dT0 = NSolve(@(dT0)TipBC(Integral(dT0)),dT0); % shooting method solution
[T,x] = Integral(dT0); % temperature profile
Once the initial temperature slope at the base of the fin is determined, either the heat transfer rate through the fin or the fin resistance can be found:
Qfin=-k*(pi*D^2/4)*dT0
Qfin = 13.930
Rfin=(Tb-Tinf)/Qfin
Rfin = 14.357
The preceding integration task can easily be done analytically. However, suppose that the radiation exchange between the fin and the surroundings were included in the analysis. In this case, the new heat equation becomes:
Heat Equation: 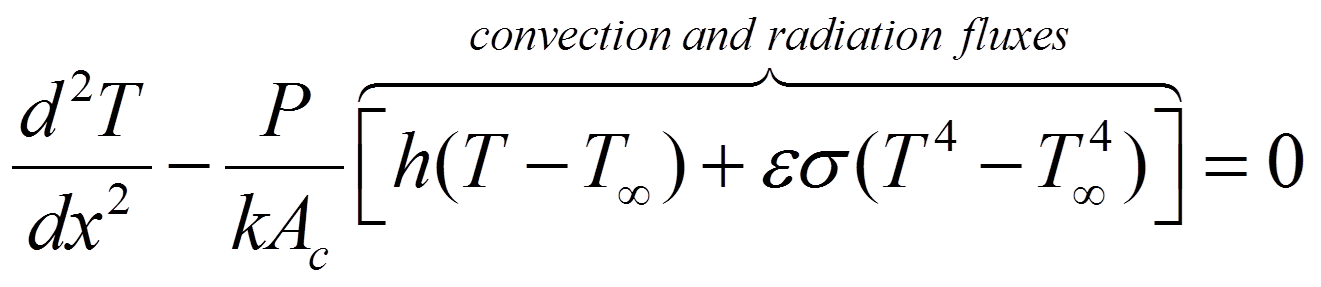 ,
,
with the boundary conditions:
BC1: ![]() and BC2:
and BC2: ![]() (tip condition) .
(tip condition) .
An analytic solution to this problem can no longer be offered. However, the changes required to the numerical solution described above are trivial:
emis=0.8; % emissivity
dTdx = @(T,x)[T(2); (P/k/Ac)*(h*(T(1)-Tinf)+emis*sig*(T(1)^4-Tinf^4))]; % heat Eq.
TipBC=@(T)[k*T(2,end)+h*(T(1,end)-Tinf+emis*sig*(T(1,end)^4-Tinf^4))]; % tip Eq.
Integral=@(dT0)RK4(dTdx,[Tb; dT0],[0, L]); % integration task
dT0 = NSolve(@(dT0)TipBC(Integral(dT0)),dT0); % shooting method
[T,x] = Integral(dT0); % temperature profile
Qfin=-k*(pi*D^2/4)*dT0
Qfin = 15.562
Rfin=(Tb-Tinf)/Qfin
Rfin = 12.852