View Factor Calculation
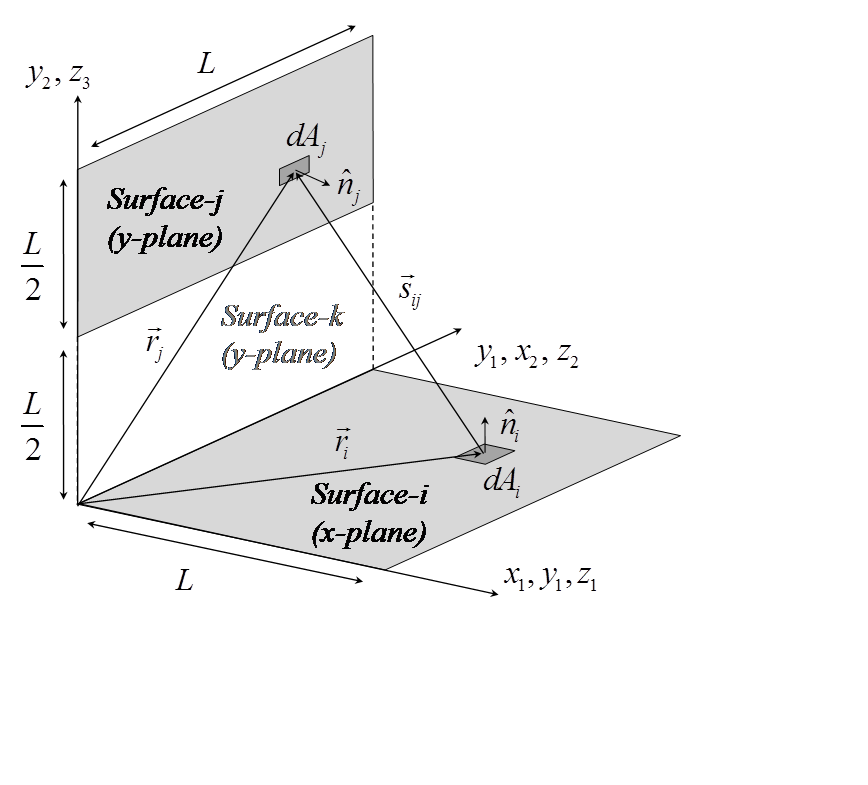 To demonstrate the use of FijCalcView( ), consider the task of numerically
integrating for the view factor between the two surfaces labeled surface-i and surface-j
in the illustration
To demonstrate the use of FijCalcView( ), consider the task of numerically
integrating for the view factor between the two surfaces labeled surface-i and surface-j
in the illustration
The vector ri sweeping out the area Ai (in the x-plane) is given by:
![]() ,
,
where ![]() .
.
The unit normal and area of dAi are given by:
![]()
and ![]() .
.
Similarly, the vector rj sweeping out the area Aj (in the y-plane), is given by:
![]() ,
,
where ![]() .
.
The unit normal and area of dAj are given by:
![]()
and ![]() .
.
The information about the integration task is provided with the definitions:
L=1;
ri=@(x)[x(1), x(2), 0];
spani=[0, L; 0, L];
ni=@(x)[0, 0, 1];
dAi=@(x,dx)dx(1)*dx(2);
rj=@(y)[0, y(1), y(2)];
spanj=[0, L; L/2, L];
nj=@(y)[1, 0, 0];
dAj=@(y,dy)dy(1)*dy(2);
The view factor is calculated with the integration task subdivided into 15 numerical steps for each spatial direction on each surface:
[Fij Ai]=FijCalcView(spani,ri,ni,dAi,spanj,rj,nj,dAj,15)
Fij = 0.053958
Ai = 1.000
This result can be confirmed with the analytic function CornerView( ):
L=1;
Fi_jk=CornerView(L,L,L);
Fik= CornerView(L,L,L/2);
Fij=Fi_jk-Fik
Fij = 0.053857