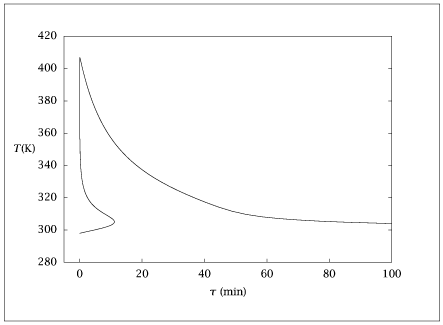
Figure 6.19:
Steady-state temperature versus residence time.
Code for Figure 6.19
Text of the GNU GPL.
main.m
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141 | % Copyright (C) 2001, James B. Rawlings and John G. Ekerdt
%
% This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
% modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as
% published by the Free Software Foundation; either version 2, or (at
% your option) any later version.
%
% This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but
% WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
% MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
% General Public License for more details.
%
% You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
% along with this program; see the file COPYING. If not, write to
% the Free Software Foundation, 59 Temple Place - Suite 330, Boston,
% MA 02111-1307, USA.
%
% limit cycle parameters
%
% units are kmol, min, kJ, K, m^3
%
% 9/10/98, jbr
%
% Revised 8/13/2018
p.k_m = 0.004;
p.T_m = 298;
p.E = 15000;
p.c_Af = 2;
p.C_p = 4;
p.rho = 1000;
p.C_ps = p.C_p*p.rho;
p.T_f = 298;
p.T_a = p.T_f;
p.DeltaH_R = -2.2e5;
p.U = 340;
p.theta = 35;
p.T_set = 321.53;
p.c_set = 0.48995;
p.T_fs = p.T_f;
p.Kc = 0;
p.gamma = p.E/p.T_f;
p.B = -p.DeltaH_R*p.c_Af*p.gamma/(p.C_ps*p.T_f);
p.beta = p.U/p.C_ps*p.theta;
p.Da = p.k_m*exp(-p.E*(1/p.T_f-1/p.T_m))*p.theta;
p.x2c = (p.T_a-p.T_f)/p.T_f*p.gamma;
%
% building the lower branch;
% use (theta,T) as dependent and
% c_A as independent
%
x0=[1; p.T_f];
nc_As = 200;
%tmp_table(1,:) = [0 T_f 0 -Inf -Inf 0];
c_Avect = linspace(0.9999*p.c_Af, .005*p.c_Af, nc_As);
for i = 1: nc_As
c_A = c_Avect(i);
opts = optimset ('MaxFunEvals', 2000*numel (x0), ...
'MaxIter', 500*numel (x0));
[x, fval, info] = fsolve(@(x) st_st_cA(x, c_A, p), x0, opts);
theta = x(1);
T = x(2);
conv = (p.c_Af - c_A)/p.c_Af;
% compute the eigenvalues of the Jacobian
k = p.k_m*exp(-p.E*(1/T - 1/p.T_m));
Jac = [-1/theta - k,...
-k*c_A*p.E/(T*T);
-k*p.DeltaH_R/p.C_ps,...
-p.U/p.C_ps - 1/theta - k*c_A*p.DeltaH_R/p.C_ps*p.E/(T*T)];
% lambda = sort(real(eig(Jac)))';
lambda = eig(Jac);
lamrow = [real(lambda(1)) imag(lambda(1)) real(lambda(2)) imag(lambda(2))];
tmp_table(i,:) = [theta, T, conv, lamrow, info];
x0 = x;
end
table = [tmp_table];
%
% turning the corner on the upper branch;
% switch to (c_A,T) as dependent and
% theta as independent
% load x with current solution
%
x0 = [c_A; T];
cortheta = theta;
nthetas = 100;
theta_vect = logspace(log10(cortheta), log10(500), nthetas);
clear tmp_table;
for i = 1: nthetas
theta = theta_vect(i);
opts = optimset ('MaxFunEvals', 2000*numel (x0), ...
'MaxIter', 500*numel (x0));
[x, fval, info] = fsolve(@(x) st_st_theta(x, theta, p), x0, opts);
c_A = x(1);
T = x(2);
conv = (p.c_Af - c_A)/p.c_Af;
k = p.k_m*exp(-p.E*(1/T - 1/p.T_m));
% compute the eigenvalues of the Jacobian
Jac = [-1/theta - k,...
-k*c_A*p.E/(T*T);
-k*p.DeltaH_R/p.C_ps,...
-p.U/p.C_ps - 1/theta - k*c_A*p.DeltaH_R/p.C_ps*p.E/(T*T)];
% lambda = sort(real(eig(Jac)))';
lambda = eig(Jac);
lamrow = [real(lambda(1)) imag(lambda(1)) real(lambda(2)) imag(lambda(2))];
tmp_table(i,:) = [theta, T, conv, lamrow, info];
x0 = x;
end
table = [table; tmp_table];
save -ascii st_st_osc.dat table;
if (~ strcmp (getenv ('OMIT_PLOTS'), 'true')) % PLOTTING
plot(table(:,1),table(:,3));
axis ([-5,100,0,1]);
figure()
semilogx(table(:,1),table(:,3));
axis([.001,1000,0,1]);
figure()
plot(table(:,1),table(:,2));
axis ([-5,100,280,420]);
figure()
semilogx(table(:,1),table(:,2));
axis([.001,1000,280,420]);
% TITLE
end % PLOTTING
|
st_st_cA.m
| function retval = st_st_cA(x, c_A, p)
theta = x(1);
T = x(2);
k = p.k_m*exp(-p.E*(1/T - 1/p.T_m));
retval(1) = p.c_Af - (1 + k*theta)*c_A;
retval(2) = p.U*theta*(p.T_a - T) + p.C_ps*(p.T_f - T) -...
k*theta*c_A*p.DeltaH_R;
|
st_st_theta.m
| function retval = st_st_theta(x, theta, p)
c_A = x(1);
T = x(2);
k = p.k_m*exp(-p.E*(1/T - 1/p.T_m));
retval(1) = p.c_Af - (1 + k*theta)*c_A;
retval(2) = p.U*theta*(p.T_a - T) + p.C_ps*(p.T_f - T) -...
k*theta*c_A*p.DeltaH_R;
|
