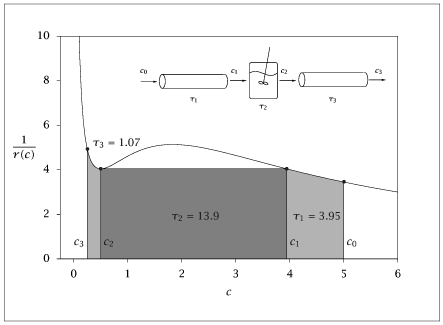
Figure 8.30:
Inverse of reaction rate versus concentration; optimal sequence to achieve 95% conversion is PFR--CSTR--PFR.
Code for Figure 8.30
Text of the GNU GPL.
main.m
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118 | % Copyright (C) 2001, James B. Rawlings and John G. Ekerdt
%
% This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
% modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as
% published by the Free Software Foundation; either version 2, or (at
% your option) any later version.
%
% This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but
% WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
% MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
% General Public License for more details.
%
% You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
% along with this program; see the file COPYING. If not, write to
% the Free Software Foundation, 59 Temple Place - Suite 330, Boston,
% MA 02111-1307, USA.
p = struct();
p.a = 5; p.b=0.05;
p.c0 = 5;
c0 = p.c0;
conv=0.95;
d = sqrt((1-2*p.b)*(1-2*p.b) - 4*p.b*(p.b+1));
w1 = (1-2*p.b + d)/(2*p.b);
w2 = (1-2*p.b - d)/(2*p.b);
x1 = sqrt(w1/p.a);
x2 = sqrt(w2/p.a);
c=linspace(0.01,10,300)';
y = 1./rxrate(c, p);
cy = [c y];
% find the outlet of the first PFR, c1, which satisfies r(c1)=1/x2
p.fixrate = rxrate(x2, p);
x0 = c0;
solveratep = @(c) solverate(c, p);
[x, fval, info] = fsolve(solveratep, x0);
info;
c1=x;
% size the first PFR, theta1 is size such that c(theta1)=c1
t0=0;
ncs=10;
cout = linspace(c0, c1, ncs);
opts = odeset ('AbsTol', sqrt (eps), 'RelTol', sqrt (eps));
pfrp = @(c, t) pfr(c, t, p);
[dummy,tout] = ode15s(pfrp, cout, t0, opts);
p.theta1 = tout(ncs);
% size the cstr, theta2= (c1-c2)/r(c2), c2=x2
c2=x2;
p.theta2 = (c1-c2)/rxrate(c2, p);
% size the second PFR, c3, which satisfies c3=(1-conv)*c0
c3 = (1-conv)*c0;
t0=0;
ncs=10;
cout = linspace(c2,c3,ncs);
opts = odeset ('AbsTol', sqrt (eps), 'RelTol', sqrt (eps));
[dummy,tout] = ode15s(pfrp, cout, t0, opts);
p.theta3 = tout(ncs);
c0; c1; c2; c3;
p.theta1; p.theta2; p.theta3;
% insert c0, c1, c2, c3 into the (c,y) table
cy = [cy; c0 1/rxrate(c0, p); c1 1/rxrate(c1, p); c2 1/rxrate(c2, p); ...
c3 1/rxrate(c3, p)];
cy = sortrows(cy);
% optimal reactor is PFR ---> CSTR ---> PFR
% theta1 theta2 theta3
% now compute segregated reactor conversion
npts = 50;
zseg = linspace(0,1,npts);
cseg0 = [c0;0];
segp = @(z, x) seg(z, x, p);
[dummy, cseg] = ode15s(segp, zseg, cseg0);
csegfin = cseg(npts,2);
% solve for cinf, which seems to be the same as what would come out of
% a cstr of theta2 with feed conc c0
x0=c0;
climitp = @(c) climit(c, p);
[x, fval, info] = fsolve(climitp, x0);
info;
cinf=x;
% now compute maximally mixed conversion
npts=50;
z=linspace(0,1,npts);
mmp = @(z, c) mm(z, c, p);
[dummy,cmm] = ode15s(mmp, z, cinf);
cmmfin = cmm(npts);
lines = [c0 1/rxrate(c0, p) c1 1/rxrate(c1, p) c2 1/rxrate(c2, p) c3 1/rxrate(c3, p) ...
c1 1/rxrate(c1, p) ;
c0 0 c1 0 c2 0 c3 0 ...
c2 1/rxrate(c2, p)];
% create the regions for filling with gnuplot
indpfr1 = cy(:,1) >= c1 & cy(:,1) <= c0;
indpfr3 = cy(:,1) >= c3 & cy(:,1) <= c2;
regpfr1 = [cy(indpfr1,:); c0 0; c1 0; c1 1/rxrate(c1, p)];
regpfr3 = [cy(indpfr3,:); c2 0; c3 0; c3 1/rxrate(c3, p)];
regcstr2 = [c2 1/rxrate(c2, p); c1 1/rxrate(c1, p); c1 0; c2 0;
c2 1/rxrate(c2, p)];
save leven.dat cy lines regpfr1 regcstr2 regpfr3
if (~ strcmp (getenv ('OMIT_PLOTS'), 'true')) % PLOTTING
plot (cy(:,1), cy(:,2), ...
lines(:,1), lines(:,2), ...
lines(:,3), lines(:,4), ...
lines(:,5), lines(:,6), ...
lines(:,7), lines(:,8), ...
lines(:,9), lines(:,10));
axis ([0,6,0,10])
% TITLE
end%if % PLOTTING
|
rxrate.m
| function rate = rxrate(c, p)
rate = c./(1+p.a*c.*c) + p.b*c;
|
solverate.m
| function retval = solverate(c, p)
retval = p.fixrate - rxrate(c, p);
|
pfr.m
| function dtdc = pfr(c, t, p)
dtdc = - 1/rxrate(c, p);
|
seg.m
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14 | function xdot = seg(z, x, p)
c = x(1);
ctot = x(2);
if (z < 1)
t = z/(1-z);
if (t <= p.theta1 + p.theta3)
pr=0;
else
pr=exp(-(t-(p.theta1 + p.theta3) )/p.theta2)/p.theta2;
end%if
xdot = [-rxrate(c, p)/(1-z)^2; pr*c/(1-z)^2];
else
xdot = [0; 0];
end%if
|
climit.m
| function retval = climit(c, p)
retval = c - p.c0 + rxrate(c, p)*p.theta2;
|
mm.m
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12 | function dcdz = mm(z, c, p)
if (z == 0.)
dcdz = 0;
else
t = (1-z)/z;
if (t <= p.theta1 + p.theta3)
f = 0;
else
f = 1/p.theta2;
end%if
dcdz = - (f*(c - p.c0) + rxrate(c, p) )/(z*z);
end%if
|
