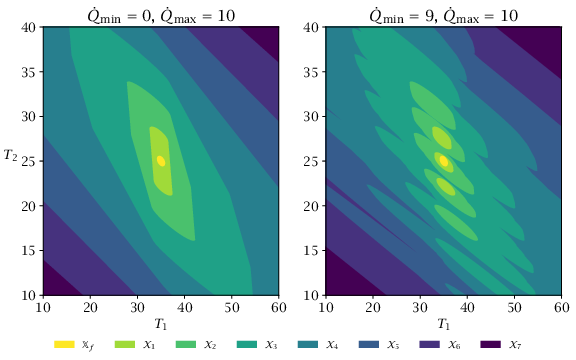
Figure 2.8:
Feasible sets \mathcal {X}_N for two values of \dot {Q}_min. Note that for \dot {Q}_min=9 (right-hand side), \mathcal {X}_N for N \leq 4 are disconnected sets.
Code for Figure 2.8
Text of the GNU GPL.
main.m
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43 | % Calculation of X_n sets for a linear system with discrete actuators.
% Note that for computational purposes, we use a polyhedral approximation of
% the true elliptical X_n.
sys = getcooler();
Qmax = sys.Qmax;
Qmin = sys.Qmin;
ns = sys.ns;
A = sys.A;
B = sys.B(:,1); % Second input doesn't affect dynamics.
F = sys.F;
P = sys.Xf.P;
xss = sys.xss;
rho = sys.Xf.rho;
Xf = ellipseterm(A, P, xss, rho, 32);
% Calculate feasible sets.
Ucontinuous = {[0, max(ns)*Qmax]};
Udiscrete = arrayfun(@(n) n*[Qmin, Qmax], ns, 'UniformOutput', false());
N = 7;
Xc = calcXn(A, B, F, N, Xf, Ucontinuous);
Xd = calcXn(A, B, F, N, Xf, Udiscrete);
% Make a plot.
fprintf('Plotting. May take some time.\n');
figure();
lims = [sys.T1ss + 25*[-1, 1], sys.T2ss + 15*[-1, 1]];
subplot(1, 2, 1);
plotXn(Xc, lims);
title('Q_{min} = 0, Q_{max} = 10');
subplot(1, 2, 2);
plotXn(Xd, lims);
title('Q_{min} = 9, Q_{max} = 10');
|
getcooler.m
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56 | function sys = getcooler()
% sys = getcooler()
%
% Returns a struct of parameters for the cooler system.
narginchk(0, 0);
% Define system.
Nx = 2;
Nu = 2;
alpha = 2;
beta = 1;
rho1 = 1;
rho2 = 1;
ns = [0, 1, 2];
Qmin = 9;
Qmax = 10;
nss = 1;
Qss = nss*Qmax;
uss = [Qss; nss];
T0 = 40;
T1ss = 35;
T2ss = 25;
xss = [T1ss; T2ss];
% Continuous-time system.
a = [-alpha - rho1, rho1; rho2, -rho2];
b = [0, 0; -beta, 0];
f = [alpha*T0; 0];
% Discretize.
Delta = 0.25;
A = expm(Delta*a);
B = a\(A - eye(2))*b;
F = a\(A - eye(2))*f;
% Choose penalty.
Q = eye(Nx);
R = eye(Nu);
% Pick terminal region.
Xf = struct('rho', 1, 'P', dlyap(A, Q)); % Level set for Xf.
% Save everything to a struct.
fields = who();
sys = struct();
for i = 1:length(fields)
f = fields{i};
sys.(f) = eval(f);
end
end%function
|
ellipseterm.m
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38 | function Xf = ellipseterm(A, P, xss, rho, n)
% Xf = ellipseterm(A, P, xss, rho, n)
%
% Returns a polyhedral tangent approximation of an ellipsoidal terminal set.
% Also makes a plot of the evolution of Xf under A.
%
% Xf is a 2 by n matrix of extreme points. A and b are the polyhedral
% representation of Xf. P is the terminal penalty weight.
narginchk(5, 5);
[v, l] = eig(P/rho);
a = 1/sqrt(l(1,1));
b = 1/sqrt(l(2,2));
calc = @(t) v(:,1)*a*cos(t) + v(:,2)*b*sin(t);
T = linspace(0, 2*pi(), n + 1);
t = linspace(0, 2*pi(), 10*n + 1);
E = calc(T);
AE = A*E;
e = calc(t);
Ae = A*e;
figure();
hold('on');
plot(E(1,:) + xss(1), E(2,:) + xss(2), '-ob', 'DisplayName', 'X_f');
plot(e(1,:) + xss(1), e(2,:) + xss(2), '--b');
plot(AE(1,:) + xss(1), AE(2,:) + xss(2), '-or', ...
'DisplayName', 'f(X_f, \kappa_f(X_f))');
plot(Ae(1,:) + xss(1), Ae(2,:) + xss(2), '--r');
xlabel('T_1');
ylabel('T_2', 'rotation', 0);
title(sprintf('Terminal Region X_f = {x | x''Px <= %g}', rho));
legend('location', 'NorthEast');
Xf = bsxfun(@plus, xss, E(:,1:(end - 1)));
|
addpoints.m
| function p = addpoints(p1, p2)
% Adds two arrays of points (2D with rows x and y).
p = bsxfun(@plus, p1, permute(p2, [1, 3, 2]));
psize = size(p);
p = reshape(p, psize(1), psize(2)*psize(3));
|
minkowski.m
| function p = minkowski(p1, p2)
% Returns minkowski sum of extreme point polytopes p and q. Only works
% for two dimensions.
narginchk(1, 2);
if nargin() < 2
p2 = [0; 0];
end
p = addpoints(p1, p2);
ch = convhull(p(1,:), p(2,:));
p = p(:,ch(2:end));
|
calcXn.m
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 | function Xn = calcXn(A, B, f, N, Xf, U, x0)
% Calculate X_n sets for the system
%
% x^+ = Ax + Bu + f
%
% Xf should be an extreme point representation of Xf, and U should be a
% cell array of extreme-point polytopes for U.
narginchk(6, 6);
Ainv = inv(A);
BU = cellfun(@(u) B*u + f, U, 'UniformOutput', false());
Xn = cell(N + 1, 1);
Xn{1} = {Xf};
fprintf('*** Calculating Xk (max k = %d) ***\n', N);
for n = 2:(N + 1)
Xn{n} = cell(length(Xn{n - 1}), length(BU));
for i = 1:length(Xn{n - 1})
xn = Xn{n - 1}{i};
for j = 1:length(BU)
bu = BU{j};
Xn{n}{i, j} = Ainv*minkowski(xn, -bu);
end
end
Xn{n} = Xn{n}(:); % Flatten to a single list.
fprintf(' k = %d: %d regions\n', n - 1, length(Xn{n}));
end
|
plotXn.m
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24 | function plotXn(Xn, lims)
% Plots a set of regions on the current axes.
narginchk(1, 2);
if nargin() >= 2
axis(lims);
end
hold('on');
if exist('viridis') == 2
cmap = @viridis;
elseif exist('parula') == 2
cmap = @parula;
else
cmap = @jet;
end
colors = flipud(cmap(length(Xn)));
for n = length(Xn):-1:1
xn = Xn{n};
for i = 1:length(xn)
patch(xn{i}(1,:), xn{i}(2,:), -n*ones(1, size(xn{i}, 2)), ...
colors(n,:), 'EdgeColor', 'none');
end
end
xlabel('T_1');
ylabel('T_2', 'rotation', 0);
|
