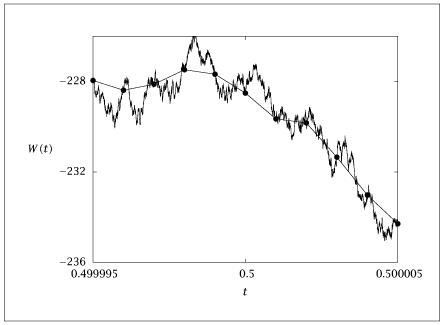
# [depends] wiener_6.dat
# This py-file loads data file 'wiener_6.dat'.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# restore the roughness to the finest time scale produced in wiener.m
# Load data
data = np.loadtxt('wiener_6.dat')
tdat = data[:, 0]
wdat = data[:, 1]
ndat = len(tdat)
# Parameters
nsam = 1000
del_ = 1 / nsam
npts = (ndat - 1) * nsam
D = 1
# Set seed for reproducibility
np.random.seed(0)
# Generate unit variance random variables
# then adjust the mean so the cumsum equals
# the difference in consecutive wdat values
raw2 = np.sqrt(2 * D * del_) * np.random.randn(nsam - 1, ndat - 1)
wmean = np.diff(wdat)
shiftmean = np.mean(raw2, axis=0) - wmean / (nsam - 1)
shift2 = raw2 - np.kron(np.ones((nsam - 1, 1)), shiftmean)
shiftnoise = np.vstack((np.zeros(ndat - 1), shift2))
wmat = np.kron(np.ones((nsam, 1)), wdat[:-1]) + np.cumsum(shiftnoise, axis=0)
w = wmat.ravel(order='F')
deltat = np.kron(np.diff(tdat), np.linspace(0, 1, nsam, endpoint=False))
tmat = np.kron(tdat[:-1], np.ones(nsam)) + deltat
time = tmat.ravel()
# The generated sequence (time, w) should pass through the data
# (tdat,wdat) but display the Wiener process roughness between the data
# points
plt.plot(tdat, wdat, '-o', label='Original Data')
plt.plot(time, w, label='Wiener Process')
plt.legend()
plt.show(block=False)
# Combine fine and rough data into a single file and arrange as matrices for np.savetxt
original_data = np.column_stack((tdat, wdat))
combined_data = np.column_stack((time, w))
with open('wexpand.dat', 'w') as f:
np.savetxt(f, original_data, fmt='%.15f', delimiter='\t', header="[rough]")
f.write("\n\n")
np.savetxt(f, combined_data, fmt='%.15f', delimiter='\t', header="[fine]")